Why Couch Potato Investing Doesn’t Work …
… For Everyone
Sorry but I couldn’t resist a trick title like that: It’s Friday; It’s overcast; It’s been raining and cold all week so few warblers are bothering to move: I’ve got to have something to smile about. However, today I will argue that for some people Couch Potato investing, also known as index investing, does not work.
What Do I Mean by Couch Potato or Index Investing?
There are several different investing methods that get lumped together under the heading index investing or Couch Potato investing. There is an absolutely fantastic website about this type of investing run by the Canadian Couch Potato at http://canadiancouchpotato.com/ for those of you who would like more information.
What I’m discussing here is a “basic” Couch Potato method of investing:
You invest in 4 types of ultra-low-cost ETFs:
- A Canadian equity fund that matches an extremely broad and diversified Canadian index
- A US equity fund that matches an extremely broad and diversified US index
- A Foreign (non-US, non-Canadian) equity fund that tries to capture a broad swath of the businesses listed on the various international stock exchanges
- A bond fund (often one with a short term-to-maturity and a mixture of government and corporate high quality bonds)
The percentage invested in each of the 4 ETFs could vary but a common split would be 20% Canadian; 20% American; 20% Foreign; 40% Bonds.
You split your money and invest it at the correct percentage in the 4 different ETFs.
Monthly, quarterly or semi-annually you add new contributions proportionately.
Once a year, you re-balance the portfolio to keep your asset allocations at 20/20/20/40. This could be done by buying more of the class that has dropped with your new contribution or by selling some of your excess units and buying more of your missing units. (E.g. if your allocation has become 30/10/20/40, you would sell some of the 30% ETF and buy more of the 10% ETF.)
You keep doing this for 10-50 years.
You do NOT sell your ETFs randomly just because the stock market is going up or down, only annually if you need to re-balance.
You do NOT invest extra in one of the 4 ETFs just because “it’s on a roll” and you want to make some extra money quickly.
Why Does Couch Potato Investing Work?
This type of index investing works because it takes all of the guess work, timing and emotion out of investing.
It’s based on the theory that over time the value of money invested in the stock markets and bonds will increase so if you invest in them and stay invested at all times, the value of your investments will increase.
Some will argue that you will even earn the most by investing in this way. That gets way too complicated for me to be interested in, but it is generally agreed by everyone that it is a very good way to invest which should result in an increased value of your savings over time.
I keep saying “over time” because at any one MOMENT in time, the value of your investments may NOT be higher. And that’s the problem.
Couch Potato Index Investing Does Not Work for Everyone
The reason couch potato index investing does not work for everyone is that not everyone can stick to it.
Some people cannot accept seeing large decreases in the value of their investments.
Other people cannot accept seeing investments not increase in value over several months or even years.
For example, following a simple Couch Potato portfolio, an investor might put 20% of their money into an International equity ETF. Let’s say they invested $10,000.
During a nasty period of market upheaval, they may see the value reported for their investment in that ETF drop to $7000.
To be a proper Couch Potato investor they must
- Shrug and ignore it, until
- during their yearly asset allocation re-balancing time
- when they must either sell some of their other ETFs to bring the percentage back up to 20% of their portfolio, or
invest new money in this ETF until it comes back up to 20% of their portfolio.
That’s right: They have to sell their “winner” and buy more of their “loser”; or put more new money into their “loser.”
Because it’s not really a “loser.” It’s just an ETF that has dropped in value. Over time, lots of time, the Couch Potato philosophy says that it will go back up in value and in fact increase in value over the starting value. So by re-balancing, the investor is actually buying more of a “bargain” ETF not a “loser” ETF. And doesn’t everyone like to buy a bargain?
Some people, though, just cannot handle this. At best they will ignore this drop in value of the international ETF and refuse to rebalance their asset allocation annually. At worst they will sell out of their entire position in this international ETF “dog” and put the money into something else.
Either way, they are no longer investing in the Couch Potato Index style.
They are not likely to succeed as a Couch Potato investor because they are ignoring the simple, basic rules that make this style work.
How Can I Decide If I Can Succeed as a Couch Potato Index Investor?
It’s really not possible to be sure how you will react to a dizzying drop in the value of an ETF until it happens. However, you can ask yourself some tough questions to get a glimpse of how you might feel.
The internet is full of great charts.
https://ca.finance.yahoo.com/echarts?s=^GSPTSE
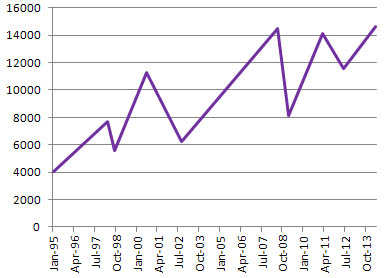
is a link to a Yahoo chart of the value of the S&P TSX Composite Canadian index. If you click on the Max link under the chart, you will see how it has behaved for many years.
https://ca.finance.yahoo.com/echarts?s=SPY#symbol=SPY;range=my
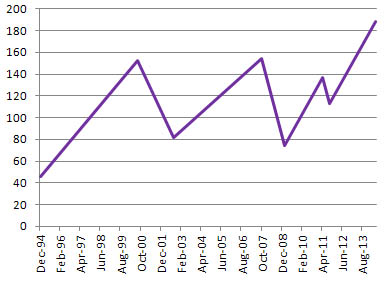
is a link to a Yahoo chart of the value of the SPDR S&P 500 NYSE. If you click on the Max link under the chart, you will see how it has behaved for many years.
It’s not just important to look at those sharp drops.
It’s also important to look at the width between two points at the same height. The width is how many months or years it took for the index to return to the SAME value. Not to increase, just to return to where it was.
Looking at the Yahoo TSX chart, if you bought units in a matching index fund only in August 2000, you’d have had to patiently wait until about December 2005 just to *break even*. (Dividends will help a bit but not as much as you might think if you buy a “most of the TSX” ETF. Many TSX stocks pay almost nothing in dividends.)
Similarly, if you bought in only at June 2008, you’d have to wait till February 2011 to break even and even then it would go down again only rebounding by September 2013.
If you bought in only during April 2011, you would only have broken even in October 2013.
The SPDR S&P 500 chart also shows the need for patience. Someone who bought only in September 2007 had to wait till early 2013 just to break even.
NOTE: These charts are not meant to represent the actual ETFs you might buy in your portfolio. They are just meant as quick examples of real market fluctuations.
Are You Brave, Patient and Stalwart Enough to be a Couch Potato?
Intestinal fortitude. That’s what you need to be a good Couch Potato index investor.
You have to be prepared to stomach more than a 30% market drop for one, or more, of your ETFs.
If you truly want to be a Couch Potato, you have to be prepared to lounge back through a 50% market drop and keep waiting, often for years, for your holdings to gradually climb back up to where you bought them at.
That means you have to wait to *break even*, not just to make a profit.
If you sell during a drop, you will almost always lose. And you are not a Couch Potato Index investor any more.
Some people who try to be Couch Potatoes panic when the markets drop. They sell low. They won’t wait years for a rebound. They then curse the markets and stalk off to invest only in GICs and savings accounts.
Regular contributions do make drops easier to weather because you buy some new units when prices are low to help offset the ones you bought when prices were high. It makes it feel like you’re making money more quickly as you wait for the re-bound.
Proper annual rebalancing is also critical and as a bonus it can obscure the cause of your paper losses. (Remember they are not TRUE losses unless and until you sell your ETFs.)
Who Does Couch Potato Index Investing Work For?
It could work for anyone, if they let it.
It certainly will work for someone who is totally dispassionate about finances and fully capable of ignoring even catastrophic market crashes because he/she understands and believes the mathematics behind this investment method.
It works for thousands of people.
It might work for you.
Am I a Couch Potato Index Investor?
No.
I won’t let it work for me: I am extremely risk averse. I know I would not be willing to watch 20% of my invested money (in any one index) drop to half its previous value.
We do use Couch Potato Index Investing within one of our defined contribution pension plans. Frankly we have no other logical choice. It’s doing reasonably well but it sure does hurt to wait out the times the markets are down and the agonizingly long time it takes for the markets to rebound. Fortunately, our bonds fund did extremely well during the last market drop which buffered the loss somewhat.
Related Reading
- How to Buy Stocks and ETFs at BMO InvestorLine
- How to Buy Stocks and ETFs at RBC Direct Investing
- How to Buy Stocks and ETFs at CIBC Investor’s Edge
Join In
Are you a Couch Potato Index investor? Or do you actively trade? Or are you a Fixed Income Only investor? Or do you take a hybrid approach? You’re probably doing reasonably well using any method if you have no debts and are steadily saving money. Please share your opinions and advice with a comment.